Selected Research
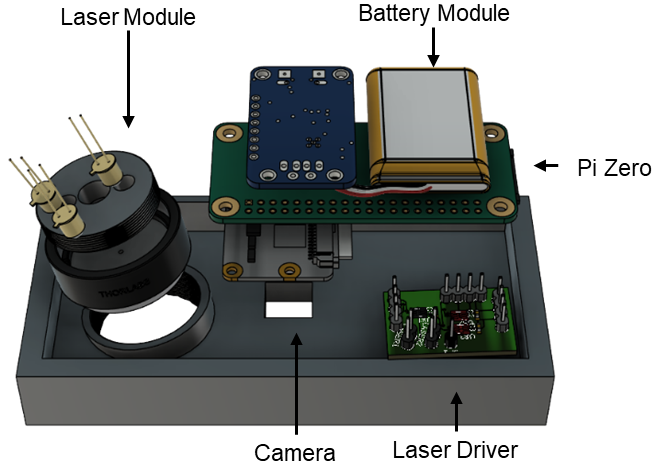
SkinSpex: A Portable Speckle Imaging System
SkinSpex is a compact, low-cost system for non-contact monitoring of heart rate, respiration, perfusion, and structural skin features such as piloerection through laser speckles. Built on a Raspberry Pi Zero 2 with a multi-wavelength laser setup (560, 750, and 930 nm), the system is designed for use in everyday and point-of-care settings. I led the design and development of the full pipeline, including hardware, embedded software, and real-time speckle analysis and validated its ability to capture acute physiological changes. The work demonstrates the potential of speckle imaging for comprehensive, wearable health monitoring in real-world environments.
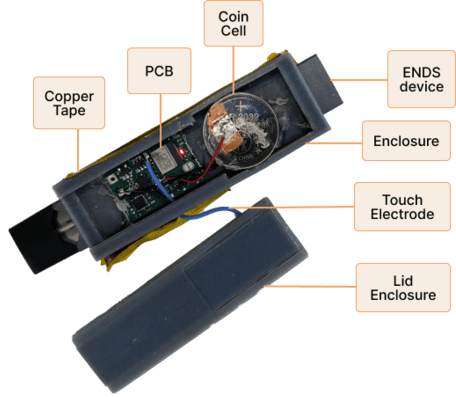
PuffEM: An E-cigarette Sleeve for Estimating User Nicotine Intake
PuffEM is a low-power, sensor-driven system designed to detect and analyze vaping behavior on electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS). By combining magnetometer, touch, and IMU sensors, it enables reliable estimation of puff timing, duration, and intensity, overcoming the limitations of gesture based and self reported methods. The system supports multidevice compatibility and was validated through both lab testing and in-wild studies, capturing over 750 puffs. My contributions focused on the hardware design, sensor integration and complete embedded firmware development to support efficient, real-time sensing across different ENDS devices.
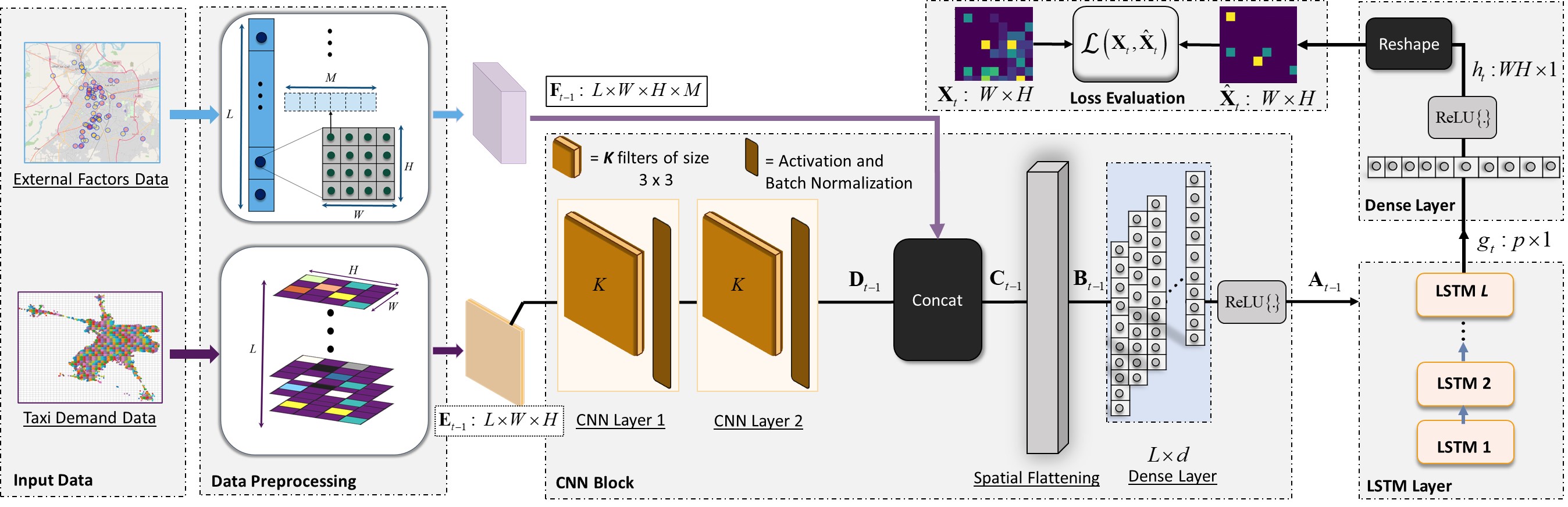
STEF-DHNet: External Factors Based Deep Hybrid Network for Enhanced Taxi Demand Prediction
STEF-DHNet is a deep learning framework for predicting regional ride-hailing demand by capturing complex spatiotemporal patterns influenced by factors like time of day, weather, and location. The model combines Convolutional Neural Networks and LSTMs to integrate external features and forecast demand trends across urban grids. Unlike traditional models, STEF-DHNet is designed to maintain high accuracy over long periods without retraining, making it more suitable for real-world deployment. I designed, implemented, and evaluated the full pipeline, including model architecture, feature engineering, and performance benchmarking across three large-scale datasets.
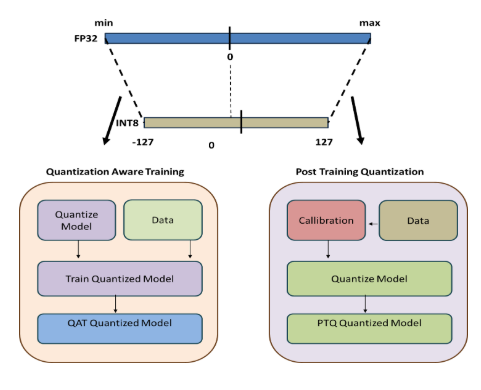
TinyMLBench: Benchmarking and Optimizing ML for Microcontrollers
This work explores the challenges of deploying machine learning models on microcontrollers and proposes a benchmarking framework tailored for TinyML applications. Focusing on image classification and wake word detection, the project evaluates a range of models including ResNet, MobileNetV1, TinyCNN, and a custom teacher-student model, across optimization techniques like Post-Training Quantization and Quantization Aware Training. Using TensorFlow Lite Micro and deploying on the Arduino Nano 33 BLE Sense, the study highlights tradeoffs between model accuracy and memory footprint, and demonstrates how carefully selected architectures and optimizations can enable practical, on-device intelligence in resource-constrained environments.
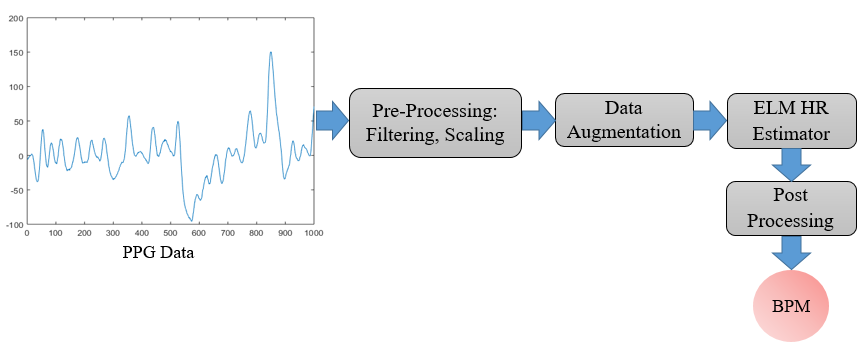
RKF-ELM: Lightweight Heart Rate Estimation Using Kalman-Aided Extreme Learning
This work explores a resource-efficient approach to heart rate monitoring from photoplethysmography (PPG) signals using a hybrid framework that combines an Extreme Learning Machine (ELM) with robust Kalman filtering. The system eliminates the need for auxiliary sensors and large scale neural networks, enabling accurate HR estimation from single channel wrist PPG, even in the presence of motion artifacts. Evaluated on IEEE and PPG-DaLiA datasets, the approach outperforms several deep learning baselines in both accuracy and computational efficiency. Its low parameter count and fast inference make it well suited for on-device deployment in wearable health monitors.
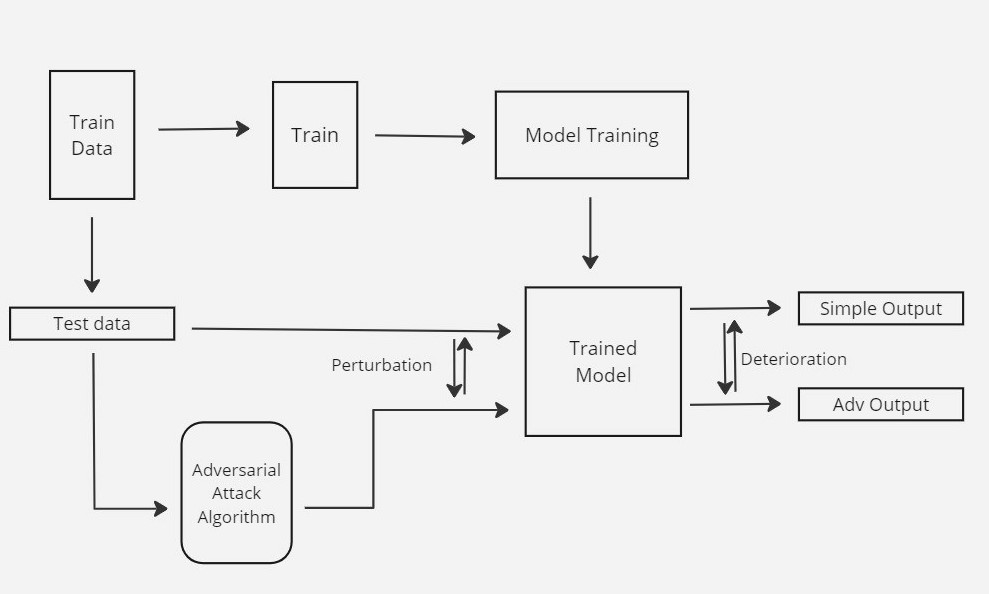
Robustness in Heart Rate Estimation: Distribution Based Attacks on PPG Time Series Models
This work investigates the vulnerability of heart rate estimation models to adversarial perturbations in photoplethysmography (PPG) time series data. We propose two new white-box attacks, Fast Distribution Attack (FDA) and Filtered Distribution Alpha Attack (FDAA), that strategically disrupt model outputs by targeting the most influential signal regions. Evaluated on IEEE and PPG-DaLiA datasets, these attacks consistently degrade the performance of both deep CNN-BiLSTM models and resource efficient ELMs, highlighting critical robustness gaps in wearable HR systems.
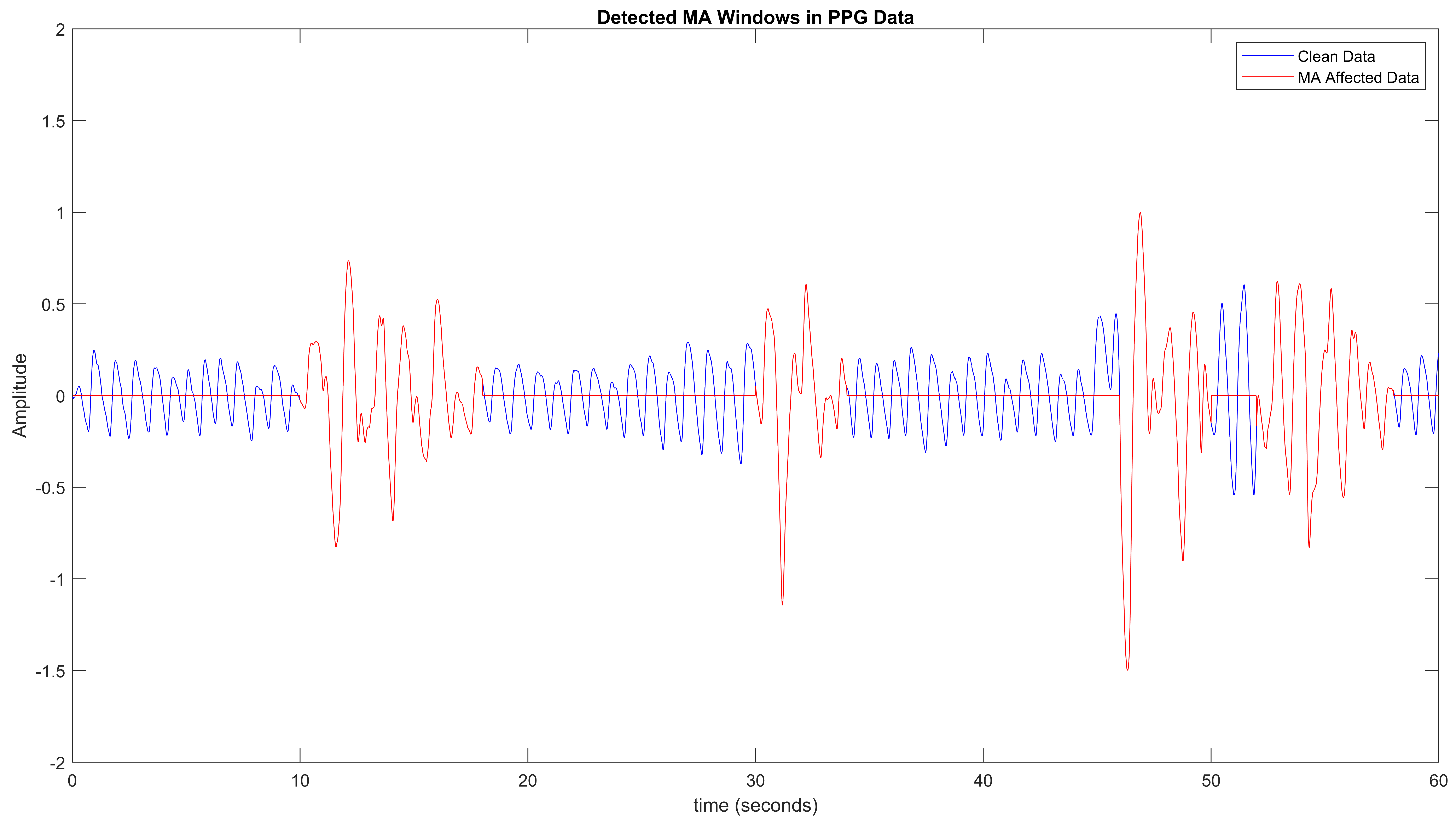
Signal Recovery from Motion: A Framework for Cleansing Wrist Worn PPG
This work presents a motion artifact removal framework for wearable photoplethysmography (PPG) signals acquired from sensors like the MAXREFDES103. The system classifies artifacts into far-wrist and near-wrist motions using statistical features (skewness and kurtosis), then applies customized denoising techniques: averaging for low-intensity motions and a combination of adaptive and notch filters for high intensity artifacts. This tiered approach improves both signal clarity and processing efficiency. Evaluated across multiple motion types and subjects, the method significantly reduces noise while preserving physiological features like R-R intervals and breathing trends, enabling more accurate heart rate and respiratory monitoring in real-world wearable settings.
Publications
- “SkinSpex: A Portable Speckle Imaging Prototype for Multiple Skin Biomarker Detection.” Sheraz Hassan, Kefan Song, Alexander T Adams. IEEE-EMBS International Conference on Body Sensor Networks (BSN), 2025.
- “PuffEM: An E-cigarette Sleeve for Estimating User Nicotine Intake.” Yiyang Wang, Rishabh Goel, Sheraz Hassan, Taegen J Doscher, Shilin Wang, Lexington Allen Whalen, Aditya S Gandhi, Yaman S Sangar, Alex Cabral, Xuhai Xu, Josiah Hester, Alexander T Adams. ACM/IEEE Conference on Connected Health: Applications, Systems and Engineering Technologies (CHASE), 2025.
- “STEF-DHNet: Spatiotemporal External Factors Based Deep Hybrid Network for Enhanced Long-Term Taxi Demand Prediction.” Sheraz Hassan, Muhammad Tahir, Momin Uppal, Zubair Khalid, Ivan Gorban, Selim Turki. *arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.14476*, 2023.